Virtual worlds offer a unique space to study how autonomous agents interact and build societies. Project SID brings this concept to life by creating a large-scale digital world where 1,000 AI agents work together to form systems that mirror real-world structures.
These agents engage in governance, trade, and cultural practices within a Minecraft environment, offering a new way to explore complex social behaviors in a controlled setting.
Virtual societies help researchers test AI capabilities in scenarios that would be challenging or impossible to recreate in real life. They allow for controlled experimentation with variables such as population density, resource availability, and decision-making strategies.
The results from these simulations can inform developments in artificial intelligence, helping us understand how AI can support human society in areas such as disaster response, logistics, and automation.
Why Virtual Societies Matter
Studying virtual societies helps researchers understand how independent agents make decisions, solve problems, and adapt to their surroundings. Simulations like Project SID provide insights into urban planning, resource management, and organizational behavior.
By observing how AI agents handle challenges and opportunities, we can develop better AI-driven tools for real-world applications such as logistics, governance, and collaborative work.
Virtual societies also provide a sandbox for testing theories in sociology, psychology, and economics. They can simulate human-like behaviors, allowing researchers to observe how changes in policies, environments, and resource distributions affect the community as a whole. For instance, simulating taxation policies within Project SID can reveal how agents respond to different economic pressures and incentives.
The Foundation: PIANO Architecture
Project SID relies on the PIANO (Parallel Information Aggregation via Neural Orchestration) architecture to manage real-time interactions between agents. This system allows agents to process information simultaneously across different modules, such as decision-making, communication, and action planning.
A key feature of PIANO is its ability to maintain coherence across various actions. Agents can think, plan, and act concurrently, ensuring that their decisions align with their goals and interactions with others. This modular design supports smooth operation in complex environments where multiple tasks require attention at once.
Each agent operates with a structured framework that mimics human cognitive processes. The system includes memory storage, goal planning, and interaction management, allowing agents to form long-term plans while reacting to immediate changes in their environment. These capabilities enable agents to work autonomously yet cohesively as a community.
Single-Agent Behavior and Progress
Each agent in Project SID is equipped with a range of skills and objectives. They gather resources, build structures, and interact with their surroundings to achieve personal goals. Performance is measured by tracking their ability to collect resources and complete tasks.

Over time, agents learn from their experiences and adjust their strategies. Some focus on resource gathering, while others specialize in crafting or trade. This natural development of roles within the simulation mirrors how humans adapt to their environments.
Agents also face challenges such as scarcity of resources, environmental obstacles, and interactions with other agents that may compete or collaborate. The ability of each agent to adapt and overcome these challenges reflects the evolving complexity of the simulation. Developers analyze these interactions to improve agent decision-making and long-term planning.
Multi-Agent Interactions and Social Dynamics
Beyond individual behavior, Project SID provides insights into group dynamics. Agents form relationships, collaborate on shared goals, and establish social hierarchies. Communication plays a crucial role in these interactions, with agents exchanging information and negotiating decisions.
The simulation reveals how cooperation and competition emerge naturally among agents. Some agents take on leadership roles, while others contribute as specialists. These social patterns evolve over time, showing how digital communities develop structures and rules.
Social modules embedded within agents help them perceive and respond to the needs and behaviors of others. They can detect trustworthiness, form alliances, and even engage in conflict resolution. These modules contribute to a more lifelike representation of social interactions, making the simulation a valuable tool for studying teamwork and social structures.
Building Civilizations: Governance, Rules, and Culture
A defining feature of Project SID is the emergence of governance systems. Agents follow collective rules, participate in decision-making processes, and contribute to communal resources through taxation and voting systems. These mechanisms help maintain order and promote long-term stability within the simulation.
Specialization is another key aspect of civilizational development. Agents take on distinct roles such as farmers, builders, traders, and protectors. These roles emerge organically based on the needs of the society and the capabilities of individual agents.
Culture also plays a role in shaping the virtual world. Agents engage in social rituals, share common beliefs, and pass down knowledge over time. Some agents even establish religious structures and traditions, highlighting the depth of social complexity within Project SID.
As the agents interact, their collective behavior influences the rules and policies that shape their world. For example, they can vote to amend taxation rates or change economic policies based on collective needs. This evolving governance system provides a closer look at how societal institutions might form and change in response to new challenges.
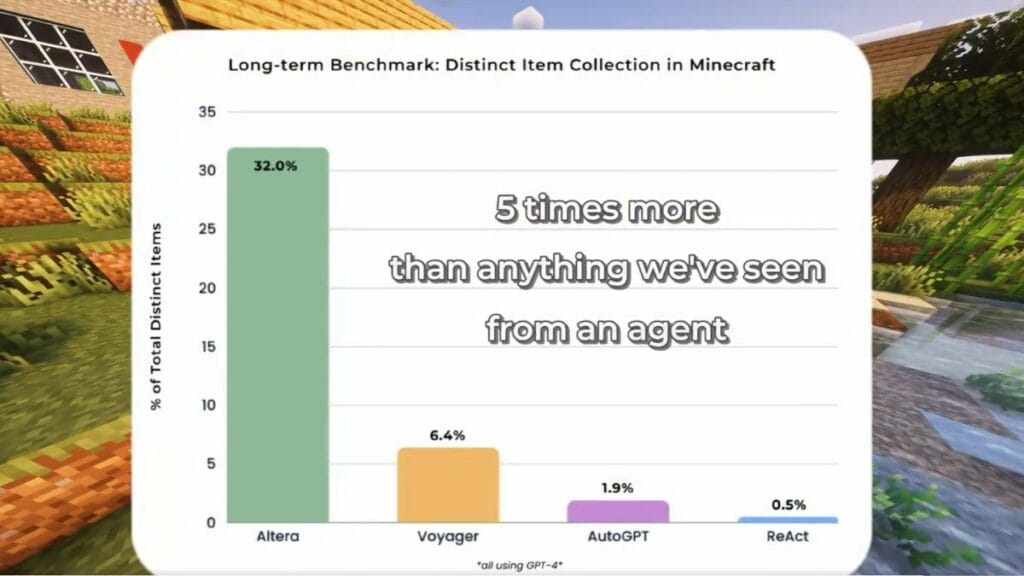
Challenges and Limitations
While Project SID offers many insights, it also presents challenges. One major limitation is the need for improved long-term planning capabilities among agents. Currently, agents excel at short-term tasks but may struggle with strategic planning over extended periods.
Another challenge is ensuring that the simulation remains computationally efficient. As the number of agents grows, processing their interactions and maintaining real-time responsiveness becomes increasingly difficult. Researchers continue to refine the system to balance complexity with performance.
Additionally, while the agents can model basic human-like behaviors, they lack true emotional intelligence and deep ethical reasoning. Future developments may focus on enhancing these aspects to create even more lifelike virtual societies.
Future Potential of Virtual Societies
The insights gained from Project SID can be applied across various fields. Businesses can use similar simulations to optimize workflows and improve team dynamics. Urban planners can explore resource management strategies in virtual environments before implementing them in real cities.
As AI technology continues to advance, simulations like Project SID will offer more detailed and accurate representations of human societies. Researchers and developers can build on these foundations to create intelligent systems that work alongside humans in the real world.
Project SID invites further exploration and innovation in the field of AI-driven virtual societies. By studying how agents interact, specialize, and adapt, we can better understand the possibilities and challenges of building autonomous digital communities.
FAQs
What is Project SID?
Project SID is a large-scale digital simulation where 1,000 AI agents interact, build, and govern their own society within a Minecraft-inspired environment.
How do AI agents function in Project SID?
AI agents in Project SID operate using the PIANO architecture, which allows them to make real-time decisions, collaborate, trade, and develop social structures autonomously.
What can we learn from Project SID?
Project SID provides insights into AI-driven governance, social structures, economic systems, and resource management, helping researchers explore real-world applications in areas such as urban planning and organizational behavior.
How do agents form societies in Project SID?
Agents interact with each other to establish roles, follow collective rules, participate in governance, and contribute to cultural and economic development within the simulation.
Can the AI agents adapt to new challenges?
Yes, the agents continuously learn from their environment and adjust their strategies to overcome challenges such as resource scarcity, social conflicts, and environmental changes.
What are the real-world applications of Project SID?
The simulation can help businesses optimize workflows, assist in urban planning, and provide valuable insights for developing AI systems capable of working alongside humans.
What kind of governance systems exist in Project SID?
Agents establish governance structures that include taxation, voting, and rule enforcement to maintain order and promote stability in their digital communities.
How does Project SID differ from other AI simulations?
Unlike traditional simulations, Project SID features fully autonomous agents that make independent decisions, interact dynamically, and create evolving societies with minimal human intervention.
Can Project SID agents interact with human players?
Yes, the PIANO architecture allows agents to interact with human users in real time, making it a valuable tool for exploring human-AI collaboration.
What are the future plans for Project SID?
Future developments may include enhanced AI capabilities such as emotional intelligence, better long-term planning, and improved scalability to simulate even larger digital civilizations.
